Overview
SmartSimple facilitates the storage of authentication credentials for various integration endpoints and external services. This functionality aims to provide a centralized configuration point for integration credentials that can be referenced throughout the system.
Notable features include native integration with services such as Salesforce and Adobe Acrobat Sign, as well as the capability to connect with any custom endpoint.
Configuring Integration Keys
Access to the Integration Key functions requires Global User Administrator permissions.
- Within SmartSimple, navigate to the Global Settings page.
- Select the Integrations tab, and under Services Settings, click on the Integration Key Management link.
- This page will display all currently configured integration keys for this instance of SmartSimple.
- To create a new Integration Key, click the + button located in the top left corner.
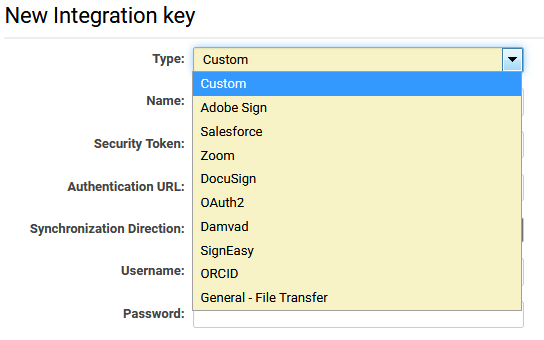
- Choose a Key Type, complete the authentication details, and click Save when finished.
Function Settings
Each new integration key includes the following fields:
- Name - A unique descriptive name for this integration key.
- Security Token - The access token or integration key provided by the external service.
- Authentication URL - The endpoint of the external service.
-
Synchronization Direction
- From SmartSimple to External Service
- From External Service to SmartSimple
- Bidirectional
- Username - The username associated with the API account.
- Password - The password associated with the API account.
For the integration with Adobe Acrobat Sign, it is necessary to input the OAuth security token and Application ID, which can be obtained by signing into your Adobe ID account at https://accounts.adobe.com. Please refer to the Adobe Acrobat Sign article in this wiki for instructions on configuring Adobe Acrobat Sign e-signature documents.
Retrieving Integration Keys
Integration keys can be retrieved from the Variable Processor using the following syntax. The ssGet variables will only be replaced when the API call is executed and will not resolve directly on the source of a page, thereby preventing the exposure of credentials to the end user.
@ssGet(APIKEY,keyname,attribute)@
An illustrative example of this would be utilizing the built-in service call function to execute a RESTful API call:
//service call syntax: //exservice_call(syncflag, callbackfunc, fields, URL) //URL - the URL to which the call is posted. //fields - contain all necessary parameters (the "svc=restful" parameter is required), delimited by ';;'. //given an Integration Key named 'myapi' exservice_call(false, "", "svc=restful;;companyid=xxx;;alias=xxx;;username=@ssGet(APIKEY,myapi,username)@;;password=@ssGet(APIKEY,myapi,password)@;;apitoken=xxx;;reportid=xxx", "https://smart.smartsimple.com.com/API/1/report/")